Hypoxia-mediated respiratory alkalosis reduces sympathetic tone, blunts hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and hypoxic cerebral vasodilation, and increases hemoglobin oxygen affinity.
- What causes respiratory alkalosis with mild hypoxemia?
- What is the cause of respiratory alkalosis?
- How does hypoxemia cause respiratory acidosis?
- How does hypoxia affect acid base balance?
- What causes Kussmaul breathing?
- Why does a pulmonary embolism cause respiratory alkalosis?
- What is respiratory acidosis and alkalosis?
- Does hypoxia cause acidosis or alkalosis?
- Why does respiratory alkalosis cause vasoconstriction?
- How does respiratory alkalosis cause hypocalcemia?
- How does body compensate for respiratory alkalosis?
- How does hypoxia affect pH?
- What is hypoxia and what are its symptoms?
- Why does high altitude cause respiratory alkalosis?
- What happens to the blood pH of a person hyperventilates?
- Can respiratory alkalosis cause seizures?
- How does pulmonary embolism cause Hypocapnia?
- What is Cheyne Stoke breathing?
- What is the mechanism that results in Kussmaul respirations?
- What causes rapid shallow respiration in respiratory acidosis?
- Does respiratory alkalosis cause metabolic acidosis?
- What labs show respiratory alkalosis?
- Why does acidosis and alkalosis occur?
- What are the complications of respiratory alkalosis?
- How does mechanical ventilation correct respiratory alkalosis?
- Why do we hyperventilate for ICP?
- What are the causes of vasoconstriction?
- What happens during respiratory acidosis?
- Why respiratory alkalosis causes Hypophosphatemia?
What causes respiratory alkalosis with mild hypoxemia?
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when you breathe too fast or too deep and carbon dioxide levels drop too low. This causes the pH of the blood to rise and become too alkaline. When the blood becomes too acidic, respiratory acidosis occurs.
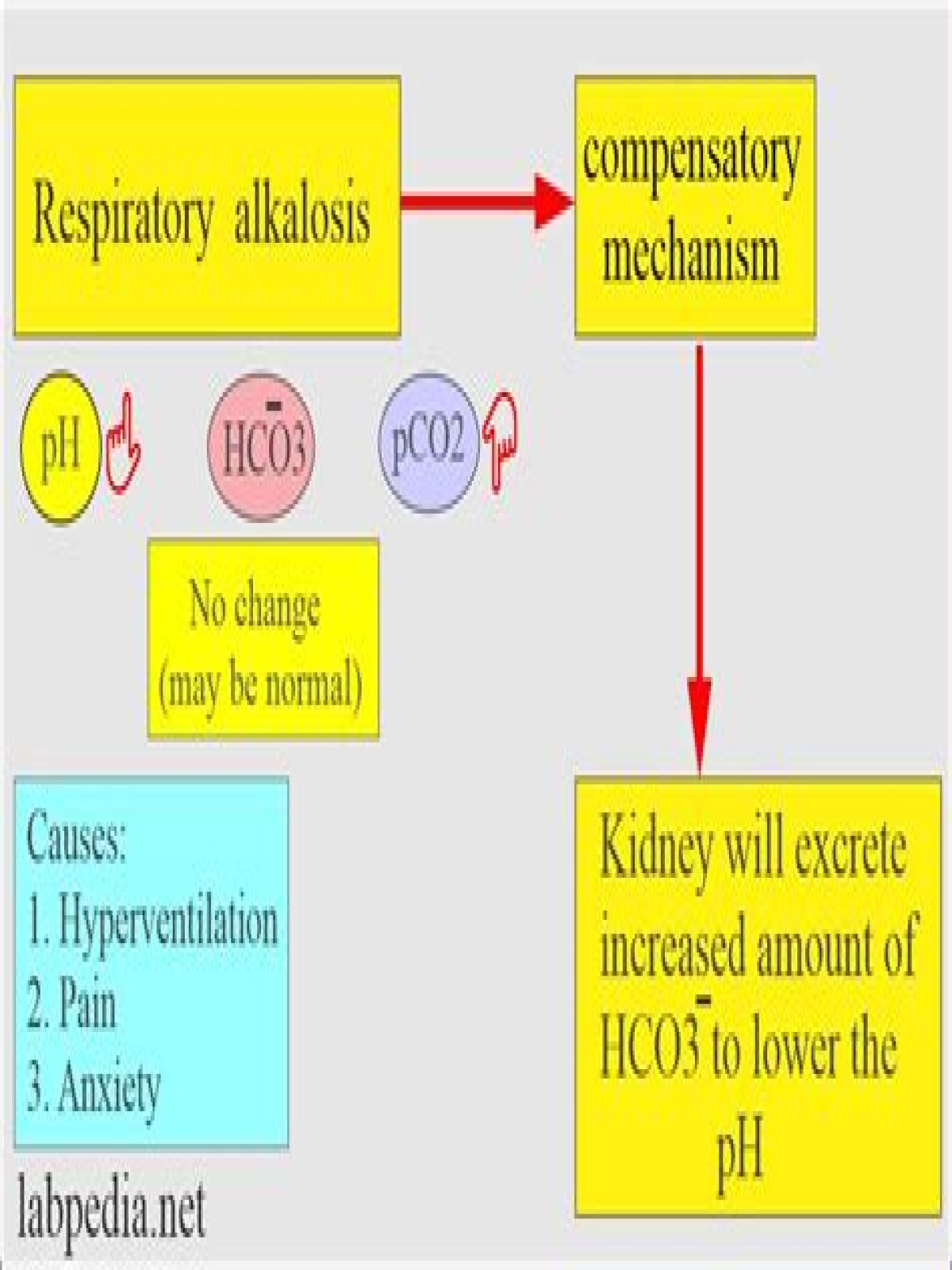
What is the cause of respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is usually caused by over-breathing (called hyperventilation) that occurs when you breathe very deeply or rapidly. Causes of hyperventilation include: Anxiety or panic. Fever.
How does hypoxemia cause respiratory acidosis?
Abstract: Most causes of respiratory acidosis are due to hypoventilation, not increased CO2 production. Respiratory insufficiency causes hypoxemia, which can lead to a secondary metabolic acidosis. The early phase of respiratory acidosis is associated with severe acidemia in acute respiratory failure.How does hypoxia affect acid base balance?
Hypoxia can lead to anaerobiosis and metabolic acidosis and, in animals that are apneic, to respiratory acidosis. A fall in blood and tissue pH is a major limiting factor in hypoxic tolerance and a variety of strategies occur in vertebrates, in concert with hypometabolism, to respond to this acid-base challenge.
What causes Kussmaul breathing?
Causes: Kussmaul breathing is usually caused by high acidity levels in the blood. Cheyne-Stokes breathing is usually related to heart failure, stroke, head injuries, or brain conditions. Pattern: Kussmaul breathing doesn’t alternate between periods of fast and slow breathing.
Why does a pulmonary embolism cause respiratory alkalosis?
Thus, most patients with PE present with a lower than normal arterial PCO2 and respiratory alkalosis because of an increased total minute ventilation. Limited data suggest that the increased total minute ventilation occurs because of reflex stimulation of irritant and juxta capillary sensors in the lung.
What is respiratory acidosis and alkalosis?
Normal human physiological pH is 7.35 to 7.45. A decrease in pH below this range is acidosis, an increase above this range is alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis is by definition a disease state where the body’s pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some respiratory or pulmonary process.[1]Does hypoxia cause acidosis or alkalosis?
Hypoxia, depending upon its magnitude and circumstances, evokes a spectrum of mild to severe acid-base changes ranging from alkalosis to acidosis, which can alter many responses to hypoxia at both non-genomic and genomic levels, in part via altered hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) metabolism.
What does respiratory alkalosis mean?Respiratory alkalosis is a condition marked by a low level of carbon dioxide in the blood due to breathing excessively.
Article first time published onWhy does respiratory alkalosis cause vasoconstriction?
Inducing hypocapnia via hyperventilation reduces the partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2), which incites vasoconstriction in the cerebral resistance arterioles. This constriction decrease cerebral blood flow, which reduces cerebral blood volume and, ultimately, decreases the patient’s ICP.
How does respiratory alkalosis cause hypocalcemia?
HVS was thought to be the main cause of hypocalcemia as intraoperative ABGA showed severe respiratory alkalosis. Alkalosis promotes the binding of calcium to albumin and can reduce the fraction of ionized calcium in the blood, and ionized calcium may reduce without changes in total calcium.
How does body compensate for respiratory alkalosis?
In response to acute respiratory alkalosis, the HCO3− decreases by 1 to 3 mmol/L for every 10–mm Hg decrease in Paco2. The kidney compensates in response to respiratory alkalosis by reducing the amount of new HCO3− generated and by excreting HCO3−. The process of renal compensation occurs within 24 to 48 hours.
How does hypoxia affect pH?
Ischemia/hypoxia generally leads to decreases in both pHi and pHo in brain cells (Tombaugh and Sapolsky, 1993; Siesjö et al., 1996; Yao and Haddad, 2004), although the pattern and magnitude of the pH changes can vary among preparations (Yao and Haddad, 2004).
What is hypoxia and what are its symptoms?
Hypoxemia occurs when levels of oxygen in the blood are lower than normal. If blood oxygen levels are too low, your body may not work properly. Blood carries oxygen to the cells throughout your body to keep them healthy. Hypoxemia can cause mild problems such as headaches and shortness of breath.
Why does high altitude cause respiratory alkalosis?
As the oxygen tension of inspired air falls with increasing altitude in normal subjects, hyperventilation ensues. This acute respiratory alkalosis, induces increased renal excretion of bicarbonate, returning the pH back to normal, giving rise to compensated respiratory alkalosis or chronic hypocapnia.
What happens to the blood pH of a person hyperventilates?
When a person hyperventilates they exhale more carbon dioxide than normal. As a result the carbon dioxide concentration in the blood is reduced and the bicarbonate/carbonic acid equilibrium shifts to the left. The corresponding drop in H3O+ concentration causes an increase in pH.
Can respiratory alkalosis cause seizures?
Summary: New research shows that febrile seizures in children may be linked to respiratory alkalosis, indicated by elevated blood pH and low carbon dioxide levels caused by hyperventilation, and independent of the underlying infection severity.
How does pulmonary embolism cause Hypocapnia?
In pulmonary embolism (PE) hypocapnia is frequent and due to hyperventilation in response to hypoxemia. But unspecific clinical presentation with isolated hypocapnia and without hypoxemia were described.
What is Cheyne Stoke breathing?
Cheyne-Stokes respiration is a specific form of periodic breathing (waxing and waning amplitude of flow or tidal volume) characterized by a crescendo-decrescendo pattern of respiration between central apneas or central hypopneas.
What is the mechanism that results in Kussmaul respirations?
What is the mechanism that results in Kussmaul respirations? Kussmaul respirations begin when acid levels in the body become too high, which is known as metabolic acidosis. The acidity level (pH) of the blood is normally in the range of 7.35 to 7.45 and is considered acidic when it drops below 7.
What causes rapid shallow respiration in respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis involves a decrease in respiratory rate and/or volume (hypoventilation). Common causes include impaired respiratory drive (eg, due to toxins, CNS disease), and airflow obstruction (eg, due to asthma, COPD [chronic obstructive pulmonary disease], sleep apnea, airway edema).
Does respiratory alkalosis cause metabolic acidosis?
Decreased Carbon Dioxide: Respiratory Alkalosis Respiratory alkalosis may result from pulmonary or nonpulmonary disease processes causing hyperventilation, or it can be a physiologic respiratory compensation for metabolic acidosis.
What labs show respiratory alkalosis?
A doctor can diagnose respiratory alkalosis using a blood test called an arterial blood gas test. They will take blood from an artery, and a special machine will then interpret the acid-alkaline content of the blood.
Why does acidosis and alkalosis occur?
Acidosis occurs when blood pH falls below 7.35, indicating an increase in hydrogen ion concentration. Alkalosis occurs when blood pH rises above 7.45, indicating a reduction in hydrogen ion concentration.
What are the complications of respiratory alkalosis?
- Arrhythmias (heart beating too fast, too slow, or irregularly)
- Coma.
- Electrolyte imbalance (such as low potassium level)
How does mechanical ventilation correct respiratory alkalosis?
In mechanically ventilated patients, hyperventilation is often the cause of respiratory alkalosis. To correct respiratory alkalosis in this situation, the clinician should decrease minute ventilation during volume-controlled ventilation by decreasing f and, if necessary, by decreasing VT.
Why do we hyperventilate for ICP?
We use hyperventilation to decrease elevated intracranial pressure (ICP) [1] and relax a tense brain (i.e. to make it smaller and softer) [2,3] because hypocapnia leads to reduced cerebral blood flow (CBF) [4] and cerebral blood volume (CBV) [5].
What are the causes of vasoconstriction?
- Prescription medicines or non-prescription medicines like decongestants. These have ingredients that cause blood vessels to narrow to provide relief.
- Some medical conditions. …
- Some psychological problems, such as stress. …
- Smoking. …
- Being outside in the cold.
What happens during respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when the lungs cannot remove all of the carbon dioxide the body produces. This causes body fluids, especially the blood, to become too acidic.
Why respiratory alkalosis causes Hypophosphatemia?
Acute respiratory alkalosis induces hypophosphatemia via changes in cellular pH. Increased pH stimulates phosphofructokinase, thus stimulating glycolysis to produce ATP, thus consuming phosphate from the cellular space. Serum phosphate is shifted intracellularly to meet this demand.