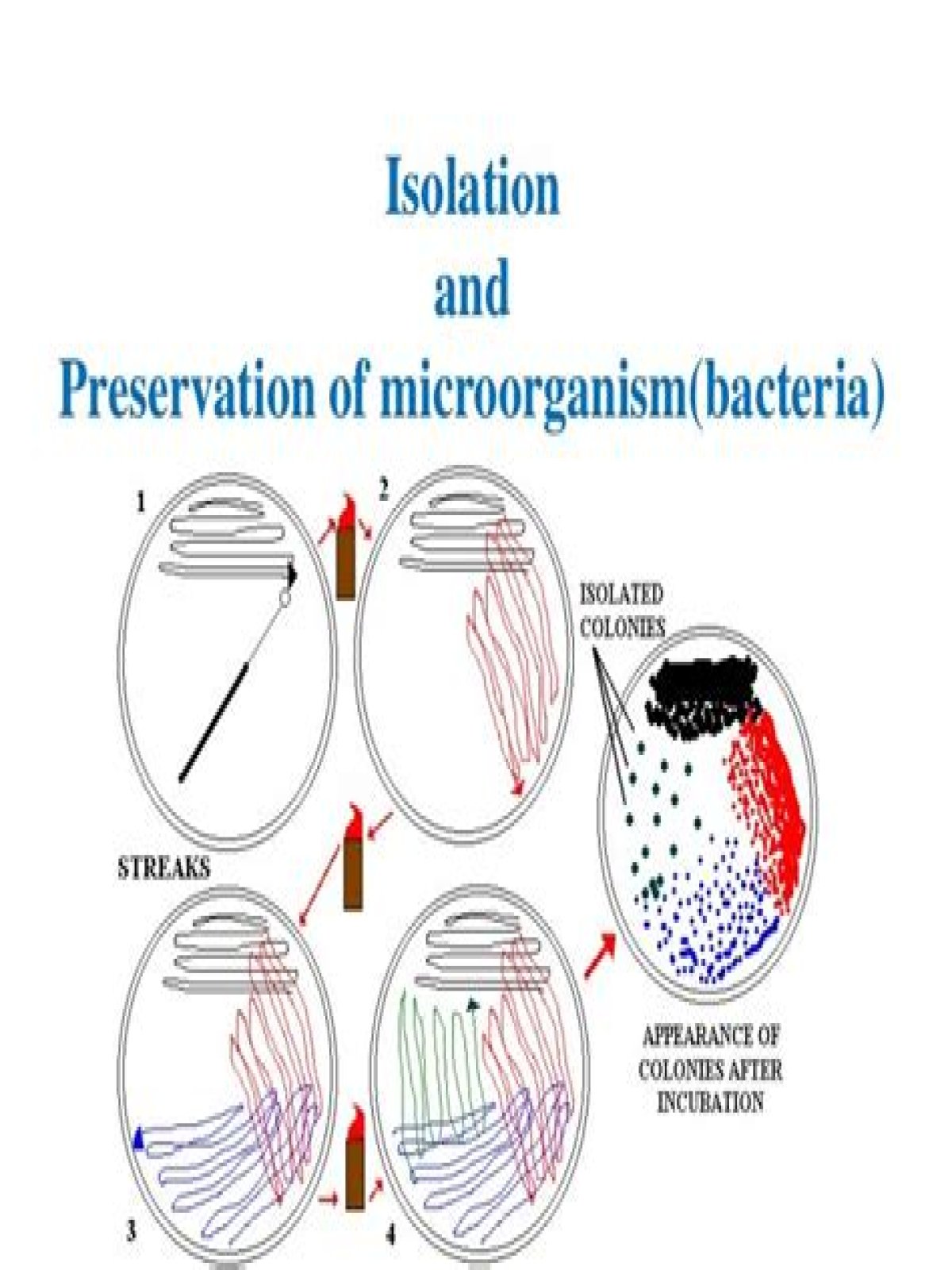
Bacterial isolation is defined as the technique of separating one species of bacteria from the bacteria’s mixed culture by different plating methods like pouring, spreading, streaking, and serial dilution.
- What is meant by a bacterial isolate?
- Why is isolation of bacteria important?
- How are bacteria isolated?
- What is the isolation technique?
- How do you identify isolate bacteria?
- Who isolated bacteria?
- How do you isolate bacteria in the air?
- What is the meaning of organism isolated?
- How do you isolate bacteria from a soil sample?
- Why is it important to start a bacterial culture with a single isolated colony?
- What are 3 types of isolation?
- What are the 4 types of isolation?
- What are the three most common isolation methods?
- Who is father of virus?
- What are the two types of bacteria?
- What is E coli isolated?
- What are 3 methods used to identify bacteria?
- Do probiotic bacteria play a positive or negative role?
- How can you detect bacteria on surfaces at home?
- What is isolation mean in biology?
- What is an example of isolation?
- What is meant by organism isolated in urine culture?
- How do you test air for bacteria?
- How do you purify bacterial culture?
- Which of the following methods could be used to isolate bacteria from a mixture?
- How do bacteria produce antibiotics?
- How do you grow bacteria in soil?
- Why is it important to have isolated bacterial colonies on a culture plate quizlet?
- What are some reasons for not getting isolated colonies from a streak plate?
What is meant by a bacterial isolate?
Bacterial isolation is defined as the technique of separating one species of bacteria from the bacteria’s mixed culture by different plating methods like pouring, spreading, streaking, and serial dilution.
Why is isolation of bacteria important?
The isolation of bacteria in pure culture is important because it facilitates the application of recombinant DNA technology through the isolation of clones.
How are bacteria isolated?
There are two main ways to isolate organisms. Streaking for isolation on an agar plate involves the successive dilution of organisms until you have the cells at a low enough density that single cells are physically isolated spatially to give rise to recognizable individual colonies.What is the isolation technique?
Cell isolation—also referred to as cell separation or cell sorting—is the process of isolating one cell population from other cells in a heterogeneous biological sample. Targeted cells are identified, isolated, and then separated according to their type.
How do you identify isolate bacteria?
THE RELATIONSHIP OF IDENTIFICATION TO BACTERIAL CLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE. In order to identify an unknown bacterial isolate, the characteristics of the isolate must be compared to known taxa. In microbiology, the basic taxonomic unit is the species, and groups of related species are placed in the same genus.
Who isolated bacteria?
In the late 1800s, Robert Koch developed techniques to cultivate and isolate bacteria cells, which were then identified and characterized by biochemical staining, microscopic observation of their morphology, and the use of enrichment cultures.
How do you isolate bacteria in the air?
Principle. The Isolation of Microorganism From Air is performed by using the settle-plate technique. In this method a suitable medium is poured over a sterile petri dish and then allow it to slidify. After that the plate is exposed to the open air for a few minutes.What is the meaning of organism isolated?
In microbiology, the term isolation refers to the separation of a strain from a natural, mixed population of living microbes, as present in the environment, for example in water or soil flora, or from living beings with skin flora, oral flora or gut flora, in order to identify the microbe(s) of interest.
What are two common isolation techniques?There are several different microbiology methods that scientists can use to isolate pure cultures of bacteria. Two common methods are streak plate and pour plate techniques.
Article first time published onHow do you isolate bacteria from a soil sample?
Weigh out 1 g of the soil sample and add it to the bottle of distilled water. Tightly cap the bottle and shake it to thoroughly mix the solution. Label the sterile test tubes “10^-3,” “10^-4,” “10^-5,” and “10^-6.” Add 9 ml of distilled water to each of the tubes, using one of the pipettes.
Why is it important to start a bacterial culture with a single isolated colony?
Why is it important to start a bacterial culture with a single, isolated colony? … to obtain single, isolated colonies of a microorganism. It is especially useful in separating a mixed culture containing two or more kinds of bacteria.
What are 3 types of isolation?
According to the CDC, the three standard categories of transmission-based precautions include contact isolation, droplet isolation, and airborne isolation.
What are the 4 types of isolation?
Four isolation categories are widely recognized –standard, contact, airborne, and droplet precautions.
What are the three most common isolation methods?
The three most common isolation methods include cotton roll isolation, rubber dam, and: dry angles.
Who is father of virus?
Martinus Beijerinck is often called the Father of Virology. Beijerinck’s laboratory grew into an important center for microbiology.
What are the two types of bacteria?
- Spherical: Bacteria shaped like a ball are called cocci, and a single bacterium is a coccus. Examples include the streptococcus group, responsible for “strep throat.”
- Rod-shaped: These are known as bacilli (singular bacillus). …
- Spiral: These are known as spirilla (singular spirillus).
What is E coli isolated?
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a bacterium commonly found in the gut of warm-blooded organisms. Most strains of E. coli are not harmful but are part of the healthful bacterial flora in the human gut. However, some types can cause illness in humans, including diarrhea, abdominal pain, fever, and sometimes vomiting.
What are 3 methods used to identify bacteria?
Traits that can be valuable aids to identification are combinations of cell shape and size, gram stain reaction, acid-fast reaction, and special structures including endospores, granules, and capsules. Traits that can be assesed with the naked eye.
Do probiotic bacteria play a positive or negative role?
Most microorganisms recognized to date as probiotics are Gram-positive, with Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium being the main species used as treatments of intestinal dysfunctions (Marco et al. 2006). However, some Gram-negatives are also used as probiotics.
How can you detect bacteria on surfaces at home?
Black lights, also known as ultraviolet lights (UV), are often used in professional cleaning to help detect if hidden pathogens are present on walls, high-touch areas, ledges, furniture, and scores of other surfaces.
What is isolation mean in biology?
Isolation. (Science: procedure) Any procedure in which a given species of organism, present in a particular sample or environment, is obtained in pure culture.
What is an example of isolation?
The definition of isolation is the state of being alone or away from others. An example of isolation is a prisoner in solitary confinement.
What is meant by organism isolated in urine culture?
Test Overview A urine culture is a test to find germs (such as bacteria) in the urine that can cause an infection. Bacteria can enter through the urethra and cause a urinary tract infection (UTI). A sample of urine is added to a substance that promotes the growth of germs. If no germs grow, the culture is negative.
How do you test air for bacteria?
There are two primary methods for microbial air sampling: Active and Passive monitoring. In active monitoring, a microbial air sampler is used to force air into, or onto its collection medium (e.g., Petri Dish with nutrient agar based test media) over a specified period of time.
How do you purify bacterial culture?
Obtaining a pure culture of bacteria is usually accomplished by spreading bacteria on the surface of a solid medium so that a single cell occupies an isolated portion of the agar surface. This single cell will go through repeated multiplication to produce a visible colony of similar cells, or clones.
Which of the following methods could be used to isolate bacteria from a mixture?
Terms in this set (61) Which of the following methods could be used to isolate bacteria from a mixture? Serial dilution followed by spread plating.
How do bacteria produce antibiotics?
Industrial microbiology can be used to produce antibiotics via the process of fermentation, where the source microorganism is grown in large containers (100,000–150,000 liters or more) containing a liquid growth medium. Oxygen concentration, temperature, pH and nutrient are closely controlled.
How do you grow bacteria in soil?
- Be a fun-guy. Use mycorrhizal inoculant. …
- Mulch it Up. Adding a layer of mulch can work wonders for garden microbes, especially if you use compost. …
- Whip Up Your Own Probiotics. …
- Open a Can of Worms. …
- Step Up to the Culture Plate.
Why is it important to have isolated bacterial colonies on a culture plate quizlet?
What is the importance of generating isolated bacterial colonies? you have to isolate the bacterial colony is you want to prove that a specific disease was due to infection with a specific microbe.
What are some reasons for not getting isolated colonies from a streak plate?
The culture plate has colonies that do not look like most of the colonies, or there are colonies where nothing was streaked. Reason: The plate has become contaminated with bacteria or fungi from the environment. is pure (free of any contaminants).